Nimrod Fortress National Park
Photo Gallery
Nimrod Fortress National Park
Introduction
Have you ever heard of a fortress so massive and mysterious? It’s tied to legends of giants, crusaders, sultans, and empires? Welcome to the full story of Nimrod’s Fortress—a mountaintop stronghold with a history as dramatic as its view.
Location
1. Nimrod Fortress National Park is situated in the midst of a magical mountain landscape on the slopes of Mount Hermon, atop a ridge 2,700 ft. or 815 m above sea level.
2. It's one of the largest and most impressive medieval fortresses in the Middle East. It controlled one of the region’s main roads, from Tyre on the Mediterranean coast, through the upper Hula Valley and Banias to Damascus.
Historical Background
1. Its Origins – 1200 AD The fortress was originally constructed around 1250 AD, during a time of great tension and transition. The Ayyubid dynasty, founded by Saladin, ruled the region following the expulsion of the Crusaders from much of the Levant.
2. In 1229, Al-Aziz Uthman, a nephew of Saladin and the Ayyubid governor of Damascus, built the original structure. His goal? To guard against the Crusader threat, especially from the military stronghold in the Kingdom of Jerusalem, and to secure the vital road to Damascus. This first phase of the fortress was a military necessity, quickly erected, with an emphasis on strong towers and strategic positioning. The Stone Mystery – Herodian Lookalikes?
-
One of the most intriguing aspects of Nimrod’s Fortress is its stonework. As you walk through the fortress, you’ll notice massive ashlar stones—finely cut blocks with a raised boss in the center and a smooth, chiseled margin around the edges. To the trained eye, these stones appear strikingly similar to those found in Herodian construction in Jerusalem, such as the Western Wall.
-
First, no archaeological evidence has ever been found on the site to suggest that a fortress or building existed here during the 1st century BC or AD, when Herod the Great ruled Judea. Instead, all the structural layers date back to the medieval Islamic period, beginning in the 13th century.
-
Second, this style of masonry wasn’t exclusive to Herod’s engineers. The Ayyubids and Mamluks often borrowed styles from the past—either for visual impact or to connect themselves with the grandeur of earlier civilizations. In this case, it’s likely that the builders deliberately imitated earlier Roman and Herodian stonework, using it to create a sense of legacy and permanence.
3. Mamluk Expansion – 1250 AD Just a few decades after the Ayyubids, the fortress saw major expansion under the Mamluks. After defeating the Mongols at the Battle of Ayn Jalut in 1260, the Mamluks secured their hold on the region. One of their generals, Baybars—who would later become sultan—oversaw significant renovations and fortifications at Nimrod’s Fortress. Under his direction, the castle grew in size, strength, and sophistication. Massive walls were reinforced, hidden staircases were added, and inscriptions were carved into the stone.
4. Ottoman Period – 1500 AD and After By 1500 AD, Nimrod’s Fortress had lost its military value. The Ottomans now ruled the region, and the fortress slowly slipped into disuse. Earthquakes damaged parts of the structure, and the forest began to reclaim it. Modern Rediscovery In the 20th century, archaeologists from the British Mandate period, and later Israel, began excavating and restoring the site. They found evidence not of ancient Israelite kings or Roman generals, but of medieval Muslim rulers who built a massive and strategic defense point overlooking vital trade and military routes.
5. Today, Nimrod’s Fortress is a protected national park. Visitors can explore its high towers, winding passages, and stone-carved inscriptions. The view from the top—over the Golan, the Galilee, and even Lebanon—is breathtaking. Legends and Misunderstandings Of course, the name “Nimrod’s Fortress” still captures the imagination. Nimrod, the mighty hunter from Genesis, was never here—but the myth persisted, because the site feels ancient, almost timeless.
6. Conclusion Nimrod’s Fortress is more than a relic of the past. It’s a monument built by medieval Muslim rulers, shaped by shifting empires, and cloaked in the aura of ancient myth. Its stones may look biblical, but they tell a medieval story—one of strategy, strength, and survival on the edge of empire.
Places of Interest
1. The Northwest Tower – The impressive gate installed in the tower bears an Arabic inscription of the Ayyubid governor al ’Aziz ‘Othman and belongs to the first stage of construction. The stones of the arch shifted in an earthquake (1759), but miraculously, the arch itself did not collapse. This “veranda” is part of a room, the ceiling of which buckled and was rebuilt in 1275 by the governor Bilik. At that time, the tower was expanded and two more stories were added. Also from this period is the opening in the tower’s ground floor leading to a cistern, above which is a shaft 7 m high; through it water was raised to the uppermost story. South of the room, a toilet was discovered. West of the gate tower, at the end of the “veranda,” a secret passage was constructed that leads outside the northern wall.
2. The Baybars Inscription – A monumental Arabic inscription, among the largest of the Mamluk period (1275). The inscription contains words of praise and eulogy for Sultan Baybars, who tasked his subordinate Bilik, commander of the fortress, with the building and reconstruction work. The inscription was placed on the facade of the second story, where Bilik’s palace was almost certainly located.
3. The Western Tower – A westward-facing tower, as yet unexcavated.
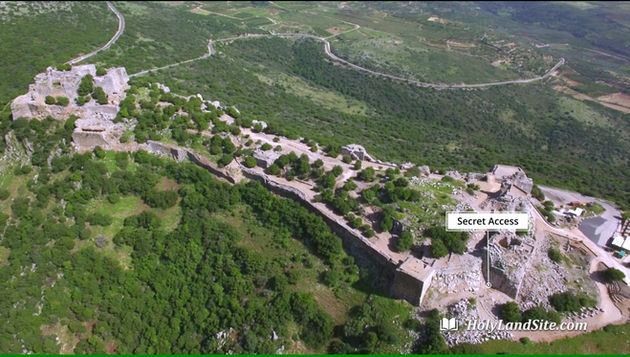
4. The Service Road – A modern pathway that passes through a breach in the wall, and through which one may directly enter the fortress.
5. The Southwest Tower – The top of this tower provides a magnificent view of the Galilee, the Hula Valley, and the slopes of the Golan. The stairs lead to the interior hall of the original tower. The tower was enlarged in Baybars’ time, after which additional embrasures for archers were built. From this hall, a spiral staircase descends to the southward-facing rooms, where you will also find embrasures.
6. The Large Reservoir – It is 9 x 25 m in area and 7 m high. Rainwater flowed into it via channels that were long since destroyed. Its northern side is roofed with a barrel vault, and stairs descend to the bottom. The southern part is roofed with a cross vault. A later breach in the southern wall, made by shepherds, permits a glimpse of the reservoir.
7. Rahat – A public drinking fountain (sabil in Arabic) located on the eastern side of the reservoir and fed by its water. Above the basin is an inscription by Fahr a-Din Hassan, who reconditioned the fountain in 1240.
8. The Beautiful Tower – This semicircular tower, which projects from the wall, was built by Baybars. The interior of the tower is octagonal, with two sides joined, resulting in a structure with seven sides. The roof of the tower is vaulted. The tower, the cut stones, and the embrasures are of outstanding construction quality. In the right-hand corner is a toilet cubicle similar to that in the northwest tower.
9. The Moat – Hewn into the bedrock, the moat separates the fortress from the donjon (the keep). The route crosses the moat in a place where it was somewhat filled in, but it can be better seen on the right side. The moat was crossed by a wooden bridge. At the end of the moat, in the southwestern corner of the donjon, is the earliest inscription found in the fortress, dating to the rule of the governor al-’Aziz ‘Othman (1228).
10. The Donjon (the keep) – A fortified, free-standing structure above the fortress. If the lower fortifications were overrun, the defenders were still able to continue defending the fortress from this massive and powerful structure. Its gate is in the northwest corner. At the four corners of the structure, square towers were erected. In the area between them, remnants of the arches of a ceremonial hall, additional halls, and water cisterns were found. From the northeast tower, a steep trail for fit hikers descends toward the park entrance.
11. The View from the Top of the Donjon – Here, one realizes the clear supremacy of the donjon over the rest of the fortress. It affords a breathtaking panorama of Mount Hermon, the Golan Heights, the Galilee, and the Hula Valley.
12. The Northern Tower (the prison tower) – This well-preserved tower was apparently also built by Baybars. It includes a central hall, with walls pierced by embrasures for archers and a staircase that ascends to the roof. From the top of the tower, Mount Hermon and Mount Dov are visible. During the 15th century, the place was apparently used as a prison.
13. The Secret Passage – The route returns to the northwestern tower (1). In the corner of the “veranda” is the entrance to a secret, graded passageway leading northward. It is 27 m long, 1.8 m wide, and has a high, arched ceiling. A row of stones can be seen on the ceiling that was displaced by an earthquake. The passage ends in an opening (postern) to the outside of the northern wall that was hidden by a pile of rocks. From here, the route returns to the western wall and goes around it on the outside to the parking lot.
14. The Pool – Located outside the fortress on its eastern side, the pool has a surface area of 26 x 54 m and a depth of at least 5 m. Its location on the slope enabled the collection of large quantities of rainwater that in peacetime served the residents of the fortress, and may even have been used for irrigation and watering flocks.
Faith Lesson from Magdala and Mary Magdalene
1. So, what are some faith lessons we can learn from this fortress site? As we walked its paths and witnessed its massive stones, we couldn't help but think of all the work and labor that went into building this massive fortress. Why did they do it? They did it to build and protect their kingdoms. At the time, it probably seemed urgent and vital to them. However, in the grand course of time, it rapidly faded away along with them and their dreams and hopes. That's what time does. As we move further away from a moment in time, that moment loses its importance and urgency. What seems so important at the moment rapidly fades away and gets lost.
2. Those who built this fortress invested an enormous amount of time, money, and even their lives. However, what do they have now? Where are they, and if they could go back in time, what would they change? I'm certain they would line the dirt paths here and share what's really important in life. Because right now, they are in one of two places according to the Bible. They are with God in paradise, or separated from Him in hell.
3. Jesus gives us eternal wisdom that we should all embrace strongly, so we don't look back and regret what we've done. He says in Matthew 6:19-21: “Do not lay up for yourselves treasures on earth, where moth and rust destroy and where thieves break in and steal, 20 but lay up for yourselves treasures in heaven, where neither moth nor rust destroys and where thieves do not break in and steal. 21 For where your treasure is, there your heart will be also.
He continues on just a few verses later in Matthew 6:33 to "seek first the kingdom of God and his righteousness, and all these things will be added to you."
4. If we are wise, we'll realize that the time we'll spend on this earth is just a drop in the bucket compared to eternity. So, what can we learn from this site? We should live our lives building God's eternal kingdom and not our own, which will quickly pass away and turn to ruins like we see at this site. We need to put God first, seek first His Kingdom and serve Him, not ourselves, our dreams, and our kingdoms.
Travel Guide Book
664 Pages
Bible Companion Book
654 Pages
Biblical Sites
Israel Overview Tour of All Biblical Sites
Jerusalem Sites
Jerusalem Model City Tour: Israel Museum
Chapel of the Ascension: Ascension & Return of Christ
Church of the Holy Sepulchre History & Background
Church of the Holy Sepulchre In-depth Tour
Death, Burial, Resurrection of Christ
Gethsemane & Church of All Nations
House of Caiaphas: Peter's Denial of Christ
Jerusalem Archaeological Site & Southern Stairs
Kidron Valley: Judgment of God
Pater Noster Church: Lord's Prayer, Olivet Discourse
Church
Prophecy, Proof the Bible Is True: Mount of Olives
Trial of Jesus: Herod/Pilate's Palace
The Old Testament Feasts & Jesus
Zedekiah's Cave & Solomon's Quarry
Sea of Galilee Sites
Capernaum: Jesus' Ministry Base
Gennesaret, Ginosar: Jesus Boat
Boat Ride: Jesus Walks on Water, Calms the Sea
Mount Arbel: The Great Commission
Sower's Cove: Parables of the Kingdom
Other Sites Around the Sea of Galilee
Northern Israel Sites
Caesarea Maritima: Holy Spirit Given to the Gentiles
Church of the Annunciation & St. Joseph Church
Mount Tabor: Transfiguration of Christ
Other Sites In Northern Israel
Central Israel Sites
Gezer: On Crossroads of the World
Jordan River: Crossing into the Promised Land
Jordan River Baptismal Site of Jesus (Qsar al-Yahud)
Judean Wilderness: Testing of Jesus
Philistine Cities of Ashkelon, Ashdod, Gaza, Ekron, Gath
St. George's Monastery (Wadi Qelt)
Valley of Elah: David & Goliath
Southern Israel Sites
Exodus, Red Sea Crossing, Mt. Sinai
The Philistines & Their City Strongholds
Other Sites In Southern Israel
Other Biblical Sites
Exodus, Red Sea Crossing, Mt. Sinai
Other Biblical Videos
Life & Ministry of Jesus Series
Jewish Holy Days & How Jesus Fulfills Them
Future of Israel: Its Wars, Conflicts, Prophecies
Shroud of Turin (Jesus). Fact or Fiction?
What Are the Differences Between Islam and Christianity?
Who Has the Rights to the Holy Land? Jews or Arabs?
What Is the Reason for the War and Conflicts in Israel and the Middle East?